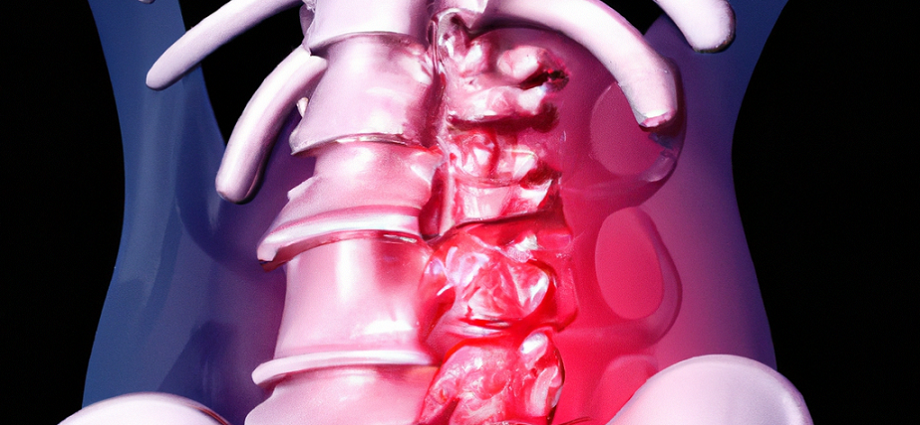
Spinal stenosis is a condition that affects the spinal canal, narrowing it and compressing the nerves that run through it. This condition can lead to symptoms such as numbness, tingling, weakness, and pain in the back, legs, or arms. If you suspect that you have spinal stenosis, it’s important to get a diagnosis so that you can receive appropriate treatment. In this article, we’ll take a look at how spinal stenosis is diagnosed.
Understanding the Symptoms of Spinal Stenosis
Before we dive into the diagnostic process, it’s important to understand the symptoms of spinal stenosis. The symptoms of this condition can vary depending on the location and severity of the narrowing. In general, spinal stenosis can cause the following symptoms:
- Pain, numbness, or tingling in the back, legs, or arms
- Weakness in the muscles that are supplied by the compressed nerves
- Loss of bladder or bowel control
It is crucial to seek medical attention promptly if you are exhibiting any of these symptoms.
Diagnostic Tests for Spinal Stenosis
There are several diagnostic tests that can be used to diagnose spinal stenosis. Your doctor will likely begin with a physical exam and take your medical history to get a better understanding of your symptoms. They may also order one or more of the following tests:
X-rays
Doctors often order X-rays as the first imaging test to evaluate the spine because they can show the alignment of the spine, the presence of any fractures or deformities, and the amount of space between the vertebrae.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
MRI is a non-invasive imaging test that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the spine. This test is often used to evaluate the soft tissues of the spine, such as the discs, ligaments, and nerves. MRI can also show the location and severity of any narrowing in the spinal canal.
Computed Tomography (CT) Scan
CT scans use X-rays and computer technology to create detailed images of the spine. This test is often used to evaluate the bony structures of the spine, such as the vertebrae and facet joints. CT scans can also show the location and severity of any narrowing in the spinal canal.
Myelogram
A myelogram is a diagnostic test that involves injecting a dye into the spinal canal to make it more visible on X-rays or CT scans. This test can be helpful in identifying the location and severity of spinal stenosis.
Electromyography (EMG)
EMG is a test that measures the electrical activity of muscles and nerves. This test can help identify which nerves are being compressed by spinal stenosis.
Nerve Conduction Study (NCS)
The NCS test measures how quickly electrical impulses move through the nerves, and it can help identify which nerves are being compressed by spinal stenosis.
Role of Your Doctor in Diagnosing Spinal Stenosis
A critical role in diagnosing spinal stenosis is played by your doctor. They will perform a thorough physical examination, take your medical history, and order any necessary diagnostic tests. Once they make a diagnosis, your doctor will collaborate with you to develop a treatment plan that suits your specific needs.
It’s important to be open and honest with your doctor about your symptoms and concerns. Don’t be afraid to ask questions or seek a second opinion if you’re not comfortable with the initial diagnosis or treatment plan.
Importance of Early Diagnosis and Treatment
Spinal stenosis is a progressive condition, meaning that it tends to get worse over time. If left untreated, spinal st enosis can lead to permanent nerve damage and disability. That’s why it’s important to get an early diagnosis and treatment to prevent further damage.
The treatment options for spinal stenosis depend on the severity and location of the narrowing. In some cases, conservative treatments such as physical therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes can help manage the symptoms of spinal stenosis. In more severe cases, surgery may be necessary to relieve the pressure on the compressed nerves.
It’s important to work closely with your doctor to develop a treatment plan that is right for you. Don’t be afraid to ask questions or voice any concerns you may have about your treatment options.
Preventing Spinal Stenosis
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent spinal stenosis, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing the condition. Here are some tips:
Practice good posture: Maintaining good posture can help reduce the strain on your spine and prevent spinal stenosis.
Exercise regularly: Regular exercise can help keep your spine healthy and prevent the development of spinal stenosis.
Maintain a healthy weight: Being overweight or obese can put extra strain on your spine, increasing your risk of developing spinal stenosis.
Avoid smoking: Smoking can damage the tissues in your spine, increasing your risk of developing spinal stenosis.
Final Thoughts
Spinal stenosis is a serious condition that can cause significant pain and disability. If you’re experiencing symptoms of spinal stenosis, it’s important to seek medical attention right away. Your doctor can perform a thorough physical exam and order any necessary diagnostic tests to determine if you have spinal stenosis.
Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent further damage and improve your quality of life. Work closely with your doctor to develop a treatment plan that is right for you, and don’t be afraid to ask questions or voice any concerns you may have. By taking an active role in your health, you can manage your symptoms and prevent further complications from spinal stenosis.